What is Flexible PCB ?
Flexible PCB stands for Flexible Printed Circuit Board (FPCB) or sometimes we just called it FPC which is made of a flexible plastic substrate, copper foil, and adhesive laminate, with very thin and high levels of bendability, tensile strength, and physical flexibility. Its lightweight, high precision, can have multiple layers of traces, and can be used to paste wafers or SMT wafers on the board. The circuitry is usually combined with electronic components such as led, IC chips, capacitors, and resistors to make the electronic product functional. Like other PCB, Flex PCB is constantly pursuing higher line density and number of layers to improve the performance of flexible boards and reduce power

Benefits of Flexible PCB
• Maximum Reliability & Durability. Flex PCB requires fewer interconnects, which in turn requires fewer contact crimps, connectors, and solder joints. It can move and flex up to 500 million times without failure. It does not contain as many potential sources of failure, which enhances its reliability, and durability
• Saving Space. Flexible PCB can be bent and concave and are thin, so they are often used for connections where there is less space and the components are more. Its’ design requires only about 10 percent of the space and weight of an ordinary circuit board assembly, offering greater installation and packaging freedom.
• Enhanced Capabilities. They are compatible with virtually any type of connector or component and work well with options such as a ZIP connector. The thermal stability of Polyimide flex materials is performing extremely well in very high temperatures, they also offer superior resistance to oils, radiation, and chemicals.
• Cost Savings. It reduced material and packaging demands, lower parts replacement costs, and assembly errors that could result in the need for repairs.
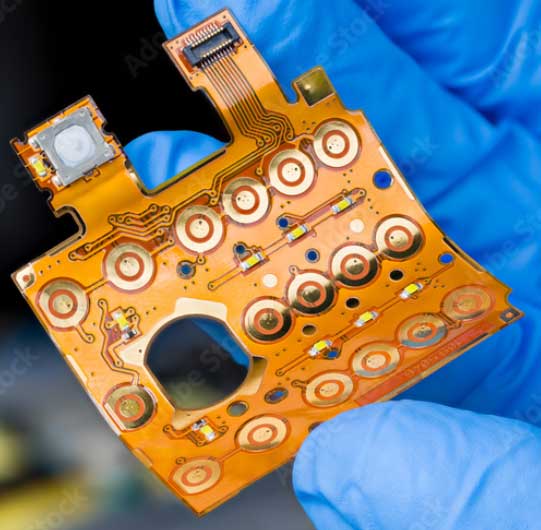

Types of Flex PCB
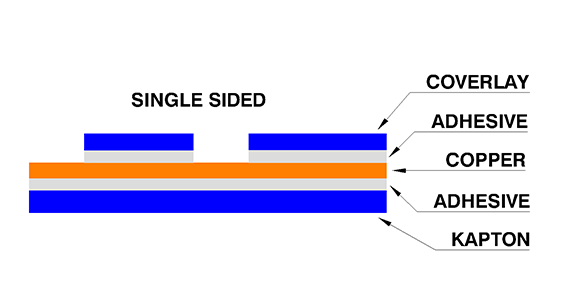
Single-sided: basic types of flexible boards, consisting of a conductor layer coated with a bonding layer, followed by a dielectric layer. Advantages include an easy manufacturing process and lower prices.
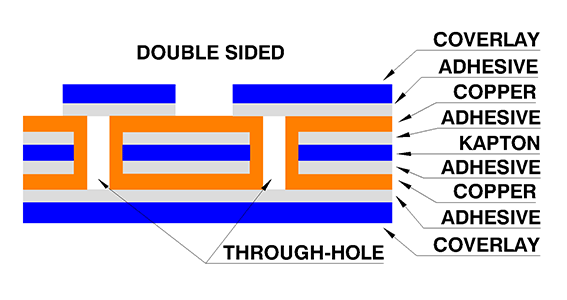
Double-sided: A double-sided substrate is used to form the circuit, and after the circuit is formed on both sides, a covering film is added to each side. the Main Benefits of double Flex PCBs is more flexibility in design, space-saving and double-sided soldering
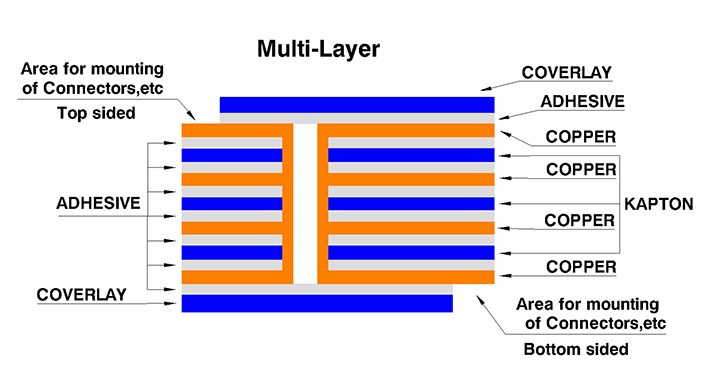
Multilayer FPC: Mainly made up of single or double panels, and drilled to allow the conductive layers to pass through, increasing the density of the circuit and improving reliability. Enables more compact package more flexible in 3D designs with PTH, blind, and buried vias.
Rigid-Flex PCB: FPC is pressed together in series between two rigid PCBs to form one printed circuit board, which is called a Rigid-flex PCB. Most rigid-flex circuit boards consist of multiple layers of flexible circuit substrates attached to rigid boards externally and/or internally. The flexible substrates are designed to be in a constant state of flexibility and are usually formed in a flexed curve during manufacturing or installation. This is dependent upon the design of the application.
Flexible PCB Structure
Flexible PCB Capability
Type | Prototypes Costs | Capability | Delivery |
US$250~ | Min Width/Spacing 2.5mil | 6 work days~ | |
US$350~ | Min Width/Spacing 3.5mil | 7 work days~ | |
according to customers’ drawing files | Min Width/Spacing 4mil | according to customers’ drawing files | |
according to customers’ drawing files | Min Width/Spacing 4mil | according to customers’ drawing files | |
Special Treatments | Tin – Plating, Nickel, Gold, EN IG, OSP/ Impedance control / EMI shield | ||
S.M.T for all kinds of active and passive components, including LED, Resistor, Diode, etc. | |||
Certification | |||
The official quotation is available on customers’ spec. & drawings Contacts: TEL: 02-22679000 #604 Email : mks@mks.com.tw | |||
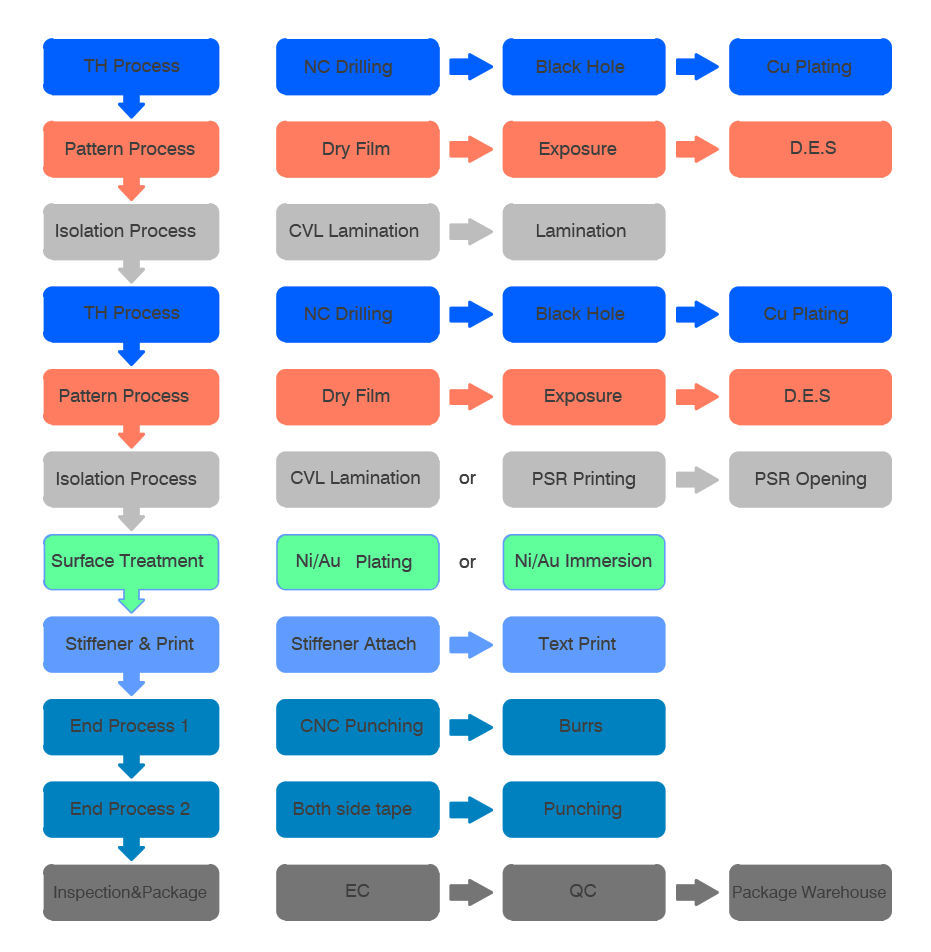
Flex PCB Manufacturing Process
Flexible PCB Material
Copper Foil
Generally, there are two kinds of Copper Foil that are often used, Rolled Anneal Copper Foil and Electrodeposited Copper Foil, thickness are 1/3oz, 1/2oz (0.7 mil), 1oz and 2oz
ED copper (Electro Deposit)
Electrolytic copper has lower cost and good electrical conductivity, but the material is more prone to fracture or breakage. For products that do not require high bendability, electrolytic copper can be used.
RA copper (Rolled Annealed copper)
The production cost is higher, but its flexibility is better. Therefore, RA is the most common material used for flexible circuit boards in high bending applications.
ED copper VS. RA copper | ||
Features | ED | RA |
Purity | 99.8% | 99.9% |
Ohm-cm | 1.8×10-6 | 1.7×10-6 |
Elongation at break | 10% | 10% |
Tensile Strength @180℃ | 20kpsi | 14kpsi |
Bend Cycles to Failure | 10~100 | 106 |
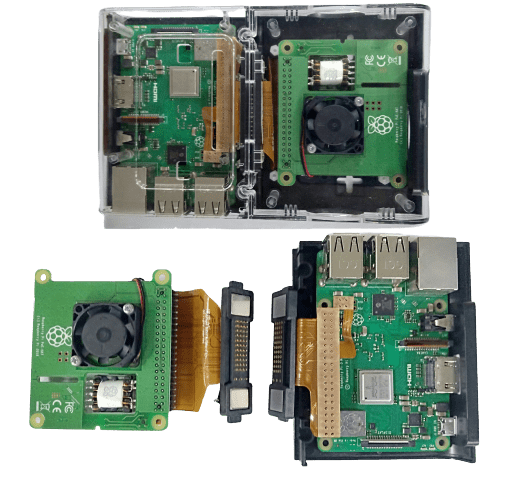
Flexible PCB Products